What insurance agency licenses will you need to start an insurance business?

What insurance agency licenses will you need to start an insurance business? | Insurance Business America
Guides
What insurance agency licenses will you need to start an insurance business?
An insurance agency license is essential if you want to start your own insurance sales business. But what types of licenses do you need? Find out in this guide
If you’re planning to start your own insurance business, one of the first and most important steps you must take is obtaining the proper licenses. Securing the right insurance agency license can be a challenging task, especially in a tightly regulated sector.
To help you sort things out, Insurance Business will give you a walkthrough of the different licenses you may need to legally operate your insurance agency. We will also explain what an insurance agency is and how it differs from other types of insurance businesses.
If you’re keen on opening your own insurance firm and currently combing through the various licensing requirements, then you’ve come to the right place. Read on and find out the different licenses you may need for your insurance agency.
Almost all businesses and professionals operating in the insurance sector need to be licensed before they can legally provide a product or service. The licensing requirements vary depending on the jurisdiction and the lines of authority a business chooses to specialize in.
Here’s a list of the most common licenses you may need to get for your insurance agency:
1. Resident insurance agency license
This type of license allows your insurance agency to operate within state lines. It works just like the licenses insurance agents and brokers need to sell insurance policies but on a business level.
2. Non-resident insurance agency license
Your insurance needs this type of license if you plan on serving clients in different states. This comes with corresponding fees and requirements. Certain states, however, have reciprocity agreements. These allow out-of-state agencies and agents to apply for licenses without the need to take the states’ licensure exam.
3. Policy-specific insurance agency licenses
Insurance agencies can choose different lines of authorities to specialize in. Generally, you will need to take out the necessary license for each line to sell policies.
The Producer Licensing Model Act (PLMA) from the National Association of Insurance Commissioners lists eight different major lines of authority, requiring separate insurance licenses.
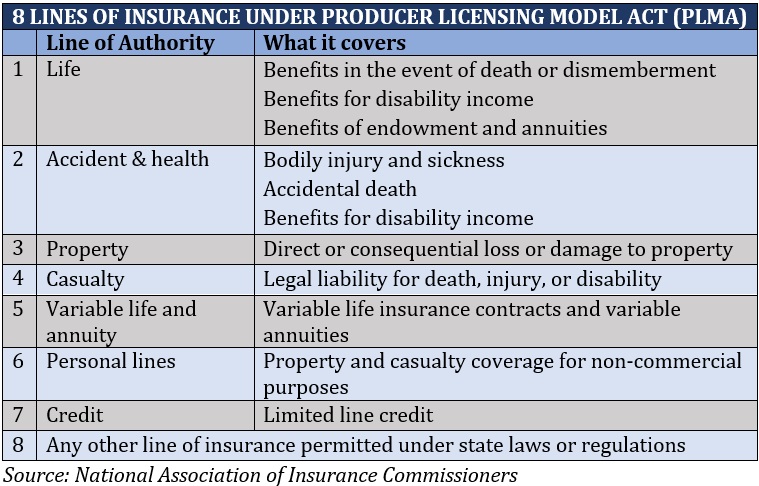
4. Surplus lines insurance agency license
This is a special type of license that enables insurance agencies to offer policies for highly complex risks that traditional insurers aren’t willing to cover. Agencies often access such products from surplus lines specialists, also referred to as non-admitted insurers.
Depending on the state and line of insurance, you may also need to assign what the industry calls a “designated responsible licensed producer” or DRLP. A DRLP is a licensed insurance professional in charge of making sure that your insurance agency complies with the laws and rules of the state you’re operating in.

Apart from insurance licenses, you may need to meet other business requirements before launching your insurance agency. These include:
General business license: Depending on the state, you may need to secure a general business license for your insurance agency to legally operate within the jurisdiction.
State registration: All insurance businesses, including agencies, are required to register as a “resident business entity” through their state insurance commissioner’s office.
Tax identification number: If your insurance agency operates as a partnership or corporation, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires you to use your federal employer identification number (FEIN) when filing taxes. If the business is structured as a sole proprietorship or single-member LLC, you may use your Social Security number.
Sign permit: If you plan on putting up signs to advertise your business, you will need to secure the necessary permits for these.
Any business or individual involved in the sale of insurance policies should have the right licenses. This must be done in each state you plan to operate.
Selling insurance without the necessary licenses can result in a felony charge, as well as substantial financial and legal penalties. These include:
fines, which vary depending on the state
blocked commissions
suspension or revocation of insurance and business licenses
Some states may likewise issue cease-and-desist orders to prevent your insurance agency from doing business. Once this happens, you may also be required to pay any unsettled insurance claims.
There are certain insurance agency employees, however, who need not get an insurance license. These include staff who exclusively perform administrative tasks such as:
assisting with paperwork
arranging meetings with clients
providing general company or policy information to customers
returning phone calls to clients
Unlicensed insurance agency employees may also be allowed to provide information about products and services to customers. This is as long as they read directly from an agency script and don’t provide interpretation. Non-licensed staff are also prohibited from receiving any compensation that’s tied to insurance commissions.
An insurance agency is responsible for selling the products of their partner insurers. It represents one or several insurance companies. An insurance agency often acts as an intermediary, providing potential buyers with information about the insurers and the products and services they offer.
Insurance agencies also have contracts with the carriers, detailing what policies they are allowed to sell and the amount they can expect to make from selling these policies. In addition, these businesses have the power to bind coverage – something most insurance brokerage firms cannot do.
There are generally two types of insurance agencies:
1. Captive insurance agencies
These businesses represent a single insurance carrier, either full-time or as an independent contractor. They may receive operational support – such as office space and administrative staff – and referrals and leads on potential buyers from these insurers.
2. Independent insurance agencies
Independent agencies work with several partner insurance companies. Since they’re not tied down to a single insurer, they can offer buyers a broader selection of insurance policies.
If running a business isn’t your thing and you prefer to practice individually instead, you can find useful tips in this guide on how to become an insurance agent.
Unlike agencies where agents are required to distribute products of their partner carriers, insurance brokerages are under no obligation to sell the policies of specific insurers. This means that they have access to a wider range of insurance products. This enables brokerages to offer customers more coverage options compared to insurance agencies.
In addition, an insurance brokerage firm acts as an intermediary between the insurance buyer and the insurer. They serve primarily as a representative of the consumers.
Insurance brokerages are responsible for helping buyers evaluate their risks and match them with the coverage that best fits their needs. And because brokerages don’t serve a single insurer, they can place policies with different providers depending on the market conditions and level of protection.
Insurance brokerage firms still owe insurance companies certain responsibilities. Because brokers offer the insurers’ products for sale, they must ensure that the information they provide insurance underwriters during the application is factual and truthful. They must also ensure the timely payments of insurance premiums. Some insurance carriers also give brokerages the power to quote, bind coverages, and handle claims on their behalf.
Here’s a summary of the key differences between an insurance agency and an insurance brokerage.

If you feel that helping insurance buyers find the right coverage is a worthwhile career, then running a brokerage firm may suit you. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to start your own insurance brokerage.
There are two ways for insurance agencies to make money:
1. Commissions
Most insurance agencies get paid through commissions. The commission amount depends on a range of factors, including:
the kind of insurance agency (captive or independent)
the type of policies they offer
number of insurance policies sold
whether the policies are new or renewals
Here’s a summary of the commission rates insurance agents receive for the different types of insurance products:

The figures above are also referred to as base commissions. Some insurance companies also offer partner agencies supplemental and contingent commissions. These are designed as incentives for agencies who help them achieve certain business targets.
Here’s how these types of commissions work:

2. Profit sharing
Some insurance companies implement profit-sharing programs for their partner agencies. Once these agencies achieve certain revenue targets, insurers typically reward them with a percentage of either written or earned premiums as a bonus.
The continued growth of the insurance industry presents a huge opportunity for those wanting to venture into the insurance business. As long as people are in need of financial protection, insurance products will always be in high demand.
But just like any type of business, starting your own insurance company entails careful planning, hard work, and dedication. If you’re an aspiring insurance entrepreneur but not quite sure where to begin, this step-by-step guide on how to start an insurance company can help.
Do you think getting an insurance agency license is an easy task? Share your thoughts in the comments section below.
Keep up with the latest news and events
Join our mailing list, it’s free!






