How much do health insurance agents make per policy?

How much do health insurance agents make per policy? | Insurance Business America
Guides
How much do health insurance agents make per policy?
How much do health insurance agents make per policy? What factors impact how much agents earn? Read on to find out the answers to these questions and more
The field of health insurance in the USA is strong and always expanding. It can seem like a pretty sure career, but you may be wondering about certain financial aspects of the job, such as how much do health insurance agents make per policy? Insurance Business will answer this question and more in this article.
The commission rates for health insurance agents vary depending on the health insurance provider they are working with. The common range is between 5% and 10% of a policy’s total premiums for the first year, with the percentage going down after a plan is renewed.
Here’s a sample calculation of how much health insurance agents make per policy for an individual health insurance plan, with annual premiums of $5,472, which is the national benchmark, according to the latest figures from Healthcare.gov.
Examples of earnings on individual health insurance policies
Annual premiums
Commission rate
Commission amount
$5,472
(National benchmark average)
5%
$273.60
10%
$547.20
Given the calculations above, a health insurance agent can earn between $273.60 and $547.20 in commissions per policy in the first year. If the commission rate drops to 1% or 2% after renewal, the agent is set of make about $54.72 to $109.44 in the succeeding years the policy is active.
For agents specializing in group health policies, which companies purchase for their employees, commission rates are slightly lower at around 3% to 6% of the total premiums. But considering that many businesses have several employees, this can translate to up to four- or even five-figure earnings per company.
The sample calculation below is for a small business with 15 employees paying $100,000 in premiums annually for a group health insurance policy.
Examples of earnings on group health insurance policies
Annual premiums
Commission rate
Commission amount
$100,000
(Small business with 15 staff)
3%
$3,000
6%
$6,000
As you can see, a health insurance agent can earn a four-figure commission from a group health insurance policy for a small business, but those who have large multinational companies as clients, the earnings can be significantly higher.
Some insurers only use captive agents to distribute their policies, particularly for individual plans. This practice, however, has become less common with the Affordable Care Act’s (ACA) health insurance marketplace becoming a popular venue for insurance agents to search for suitable coverages for their clients.
In terms of salary, most of the employment websites Insurance Business referred to estimate an agent’s annual average salary to be around $46,000 to $55,000. Apart from commission rates, how much health insurance agents make is influenced by several factors, including their experience level and where they sell policies.
The table below shows the percentile wage estimates for health insurance agents in the country based on this website.
How much do health insurance agents make – lowest to highest salary range
PERCENTILE WAGE ESTIMATES (HEALTH INSURANCE AGENTS)
Percentile
Annual wage
Monthly wage
Weekly wage
Hourly wage
10th
$28,750
$2,395
$553
$14
25th
$41,000
$3,416
$788
$20
50th (Median)
$55,188
$4,599
$1,061
$27
75th
$60,000
$5,000
$1,153
$29
90th (Top earners)
$88,500
$7,375
$1,701
$43
According to the site, the bulk of health insurance agents earn average salaries between the 25th and 75th percentiles, or about $41,000 to $88,500 per year. Wage figures below or above this range are considered outliers.
Each state implements different requirements for healthcare coverage, which can directly affect an agent’s earning potential. Here’s a list of the highest- and lowest-paying states for health insurance agents based on median salaries.
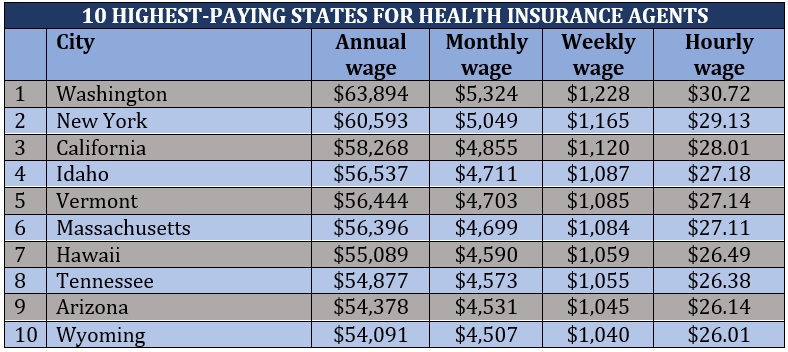
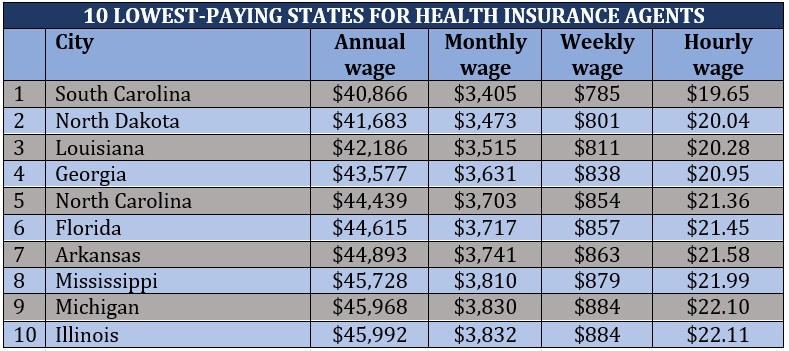
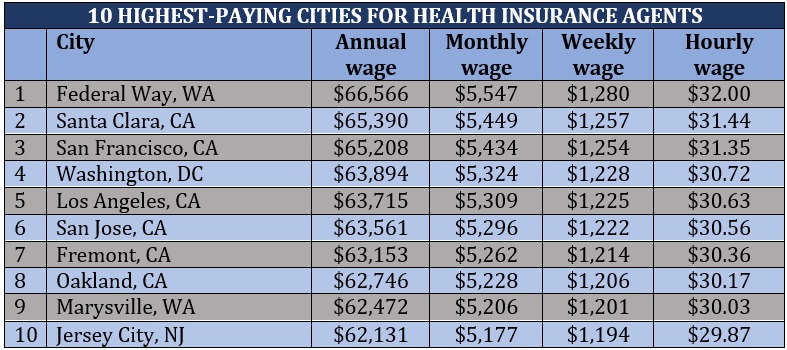
The table below shows how much health insurance agents make in the highest-paying cities across the US.
Health insurance agents act as a representative of one or more providers, selling health policies on the insurers’ behalf. These licensed professionals are tasked to explain the key features and benefits of different health plans to potential clients, assisting them in finding policies that cater to their unique needs.
This duty is somewhat similar to that of an insurance broker. But while agents work on behalf of the insurance companies, brokers are tasked to act in the best interests of the insurance buyers.
Some of the other general responsibilities of a health insurance agent include:
Screening and interviewing potential clients
Assessing existing clients’ policies for any needed additions or changes
Calculating premiums and presenting quotes to clients
Customizing health insurance plans to meet each client’s coverage needs
Handling policy renewals
Help clients in settling claims
Keeping customer records updated and organized
Due to the high cost of healthcare in the USA, health insurance has become an essential financial tool for many Americans to afford necessary medical care. A health insurance agent also plays an important role in helping citizens find affordable health insurance plans that match their needs.
The path to becoming a health insurance agent has minimal entry barriers, but once there you will need to earn various certifications to progress in your career. Here are some of the steps you need to follow if you want to pursue a career as a health insurance agent:
Finish your education: To be a health insurance agent, you must at least have a high school diploma or GED certification. A college degree can help improve your job prospects but isn’t necessarily required.
Complete a background check: Some states require insurance companies and agencies to run backgrounds on prospective agents. These include checking criminal records, credit history, previous employment, educational records, and drug test results.
Get your license: Each state has different licensing requirements for insurance agents, so it is best to check with your state’s insurance department to find out what the exact qualifications are. If you’re planning on working with the ACA’s health insurance marketplace, you must have the appropriate certification and complete the exchange’s yearly training.
Pick a health insurer to work for: Most insurers, including the largest health insurance providers in the US, use marketing organizations to find prospective agents. The marketing organizations help get you appointed to an insurance company. Many regional health insurers, meanwhile, can be contacted directly. Regardless of size, insurers may have their own employment requirements.
Pursue further education: Health insurance agents must complete continuing education (CE) to keep their licenses active. CE courses also vary between states.
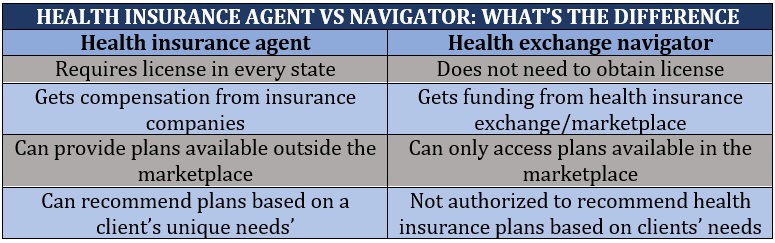
Health insurance navigators – also referred to as government exchange navigators – assist people in obtaining coverage through the ACA’s health insurance marketplace, as well as help those who are already enrolled with different issues regarding their coverage, much like what health insurance agents do.
Navigators also educate clients about the different coverages available and help them determine if they qualify for Medicaid, the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), and other government subsidies in the exchange.
Unlike health insurance agents, however, navigators cannot offer plans that are not available in government exchanges. Insurance agents, on the other hand, can show clients – as long as they are not using subsidies – other ACA-compliant health policies only accessible outside government exchanges.
And while health exchange navigators are trained and certified by the marketplace, they are not licensed by the state the way that health insurance agents are. This means that navigators cannot provide policy recommendations unlike agents can and are there instead to offer clients impartial information to help them make decisions about what plan will best suit their needs.
In addition, navigators do not receive any compensation from health insurance companies. Navigator organizations instead get funding from the health insurance exchange.
The table below lists the main differences between a health insurance agent and a health exchange navigator.
The ACA was enacted in 2010, which was designed to reduce healthcare costs to ensure that more American families can access health insurance. The law enables patients who may lack coverage due to pre-existing conditions or limited finances to get affordable insurance through their state’s health insurance marketplace.
Through these marketplaces, patients can choose from a range of health plans to suit their different needs. These include:
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): Limits coverage to care from doctors who work for or are contracted with the HMO, except during an emergency. Plans may also require that a policyholder live or work in its service area to be eligible for coverage.
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO): A managed care plan, which covers services only if the doctors, specialists, or hospitals are in the plan’s network, except in cases of emergency.
Point of Service (POS): Policyholders pay less if they access doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare providers belonging to the plan’s network. It also requires policyholders to get a referral from their primary care doctor to see a specialist.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): Policyholders to pay less if they choose to get treatment from providers in the plan’s network, but they can also access doctors, hospitals, and providers outside of the network without a referral for an additional cost.
Health insurance plans are also available in four categories based on how the costs are split between the policyholder and the insurer. Also called the “metal tiers,” these plans are:
Bronze: 60% health insurer, 40% policyholder
Silver: 70% health insurer, 30% policyholder
Gold: 80% health insurer, 20% policyholder
Platinum: 90% health insurer, 10% policyholder
If you want to know what health insurance in the US covers, and how healthcare coverage works in other countries, you can check out our global health insurance guide.
Being a health insurance agent can be a rewarding career because it gives one an opportunity to help people in times of need and make a positive impact on their lives. If you want to pursue a career as a health insurance agent, the internet is a good place to start. Do a quick online search and you can find hundreds, if not thousands, of vacancies for health insurance agents.
Do you think being a health insurance agent is a worthwhile career? Were you surprised to learn how much health insurance agents make per policy? Share your thoughts in the comments section below.
Keep up with the latest news and events
Join our mailing list, it’s free!






