How business insurance can help your company navigate difficult times

We encourage insurance agents and brokers to share this article with their clients to help them decide which business insurance policies are essential to keep them protected.
One of the biggest advantages of taking out insurance for businesses is the financial protection it provides when unexpected losses occur. As they carve out the path to success, companies may face situations that can adversely impact their profitability. Mistakes can lead to costly lawsuits, while accidents and calamities can take a huge chunk out of their revenue. Having the right policies plays a crucial role in helping their business recover faster.
Carrying business insurance also boosts a company’s credibility as many stakeholders and clients prefer working with businesses that they know are financially protected.
Taking out business insurance, however, is just one facet of how companies can minimize their losses. Pairing insurance coverage with good risk management practices is often the best way businesses can protect their assets and finances.
Embed: <iframe width=”885″ height=”498″ src=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/1sRL61C0r4Y” title=”Business Insurance: A Quick & Easy Overview” frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture” allowfullscreen></iframe>
Because each business faces their own share of unique risks and challenges, there is no one-size-fits-all policy that covers every need. The type of insurance that companies will require depends on several factors, including their business activities, size, and location.
Business insurance providers offer a range of policies that can help protect companies against the different risks they face. The selection is diverse, but according to industry insiders, these are some of the most essential coverages that businesses need to maintain their operations when accidents and disasters strike.
1. General liability insurance
General liability insurance, also called business liability or public liability coverage, protects companies against claims of bodily injury or property damage resulting from their business activities. This type of policy may also provide coverage for reputational harm and copyright infringement.
2. Professional liability insurance
Also known as errors and omissions (E&O) or malpractice insurance, this form of coverage protects the business from work-related claims, including mismanagement, sexual harassment, and discrimination. It covers legal and settlement costs arising from service-related mistakes and oversights, breach of contract, unfinished work, and budget overruns, among others.
Professional liability insurance not only covers directors and executive management but also other staff and the business itself. Although not always legally required, having this form of coverage is essential for many companies, especially for those that provide expert or advisory services.
3. Product liability insurance
For businesses that sell products, product liability coverage may be worth considering. This protects the company against lawsuits from customers claiming losses or injury because of their product. This type of commercial insurance policy also covers legal defense costs and compensation if the business is found to be at fault.
4. Directors’ and officers’ (D&O) insurance
D&O insurance, also referred to as D&O liability insurance, is designed to protect the directors and senior management of a company against financial losses resulting from business-related lawsuits. This type of policy pays out for monetary losses from these legal actions, including defense costs, settlements, and fines.
D&O coverage comes in three main types, also referred to as insuring agreements or sides, with each offering different levels of protection:
Side A: Covers “non-indemnifiable loss” or situations where the business cannot indemnify its directors or officers, either due to bankruptcy or because they are not legally allowed to do so.
Side B: The most commonly accessed insuring agreement, this works by reimbursing a company after it has compensated a director or other senior management for a loss, including defense costs, settlements, and judgments.
Side C: Also called entity coverage, this provides direct coverage for a business when both the company and its directors and senior management are named in a lawsuit.
5. Commercial property insurance
Commercial property insurance, also referred to as business property or commercial building insurance, is designed to minimize disruption to a company’s day-to-day operations by providing compensation for damages or losses that happen to the following:
Property or building the business operates in
Equipment and technology the company uses
Inventory of products and materials the business stores and sells
Some policies also pay out a portion of lost income if the damage prevents a business from conducting its usual operations. Business property coverage is often a requirement for commercial leasing arrangements.
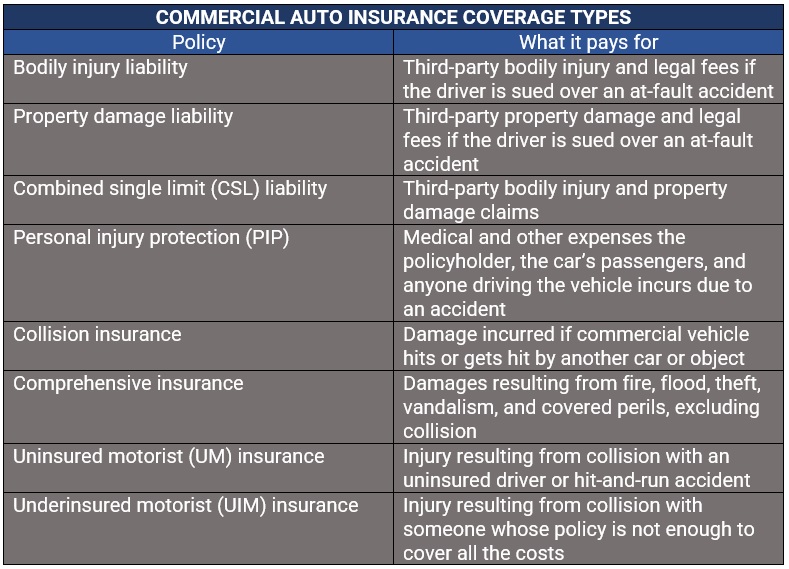
6. Commercial auto insurance
Commercial auto insurance is a type of car policy designed for vehicles driven for business purposes. In terms of protection, it works similarly to personal auto insurance but covers mainly company cars and commercial trucks and vans.
7. Health insurance
Businesses that employ more than 50 full-time staff are required to take out health insurance for their workers, according to the Affordable Care Act (ACA). For those with less than 50 employees, the ACA offers a Small Business Health Options Program (SHOP) as coverage.
8. Workers’ compensation insurance
Workers’ compensation insurance, also called workers’ comp coverage, pays out the cost of medical care and part of the lost income of employees who get sick or injured while performing their jobs. It also protects the businesses from the financial liability of having to pay for expenses arising from work-related illnesses and injuries out of pocket.
Workers’ compensation insurance policies provide several types of coverages, including:
Medical expenses: Covers the cost of medical treatment for the sick or injured worker.
Lost income: Pays out part of the employee’s wage if they need to take time off from work because of the illness or injury they sustained.
Ongoing care: Covers expenses incurred if the employee requires extended medical care due to a work-related injury or illness, including rehabilitation costs.
Disability benefits: Covers medical bills and some lost wages of employees who become disabled because of a workplace accident.
Death benefits: Pays out funeral and burial expenses and provides financial benefits for beneficiaries of employees who die due to a job-related injury or illness.
9. Business interruption insurance
Business interruption insurance, also called BI or business income coverage, is designed to protect companies against financial losses incurred from the disruption of their operations resulting from an insured peril. We will discuss this type of policy in detail in our coverage highlighted below.
10. Cyber insurance
Cyber insurance plans are designed to protect businesses against financial losses resulting from cyber incidents. Policies typically provide two types of protection:
First-party coverage
This type of coverage pays out for the financial losses the business incurs due to a cyber incident, including:
Cost of responding to a data breach
Cost of restoring and recovering lost or damaged data
Lost income resulting from business interruption
Ransomware attack payments
Risk assessment of future cyberattacks
Cost of informing customers about the cyber incident
Anti-fraud services
Third-party coverage
This provides financial protection against lawsuits filed by third parties, including customers, employees, and vendors, for damages caused by a cyberattack on the business. Policies typically cover court and settlement fees, and regulatory fines.
Every year, insurance behemoth Allianz surveys thousands of businesses from about 90 countries and territories and more than 20 industries to find out which risks these companies see as posing the greatest threat to their operations. Here are the 10 biggest risks businesses across the globe are facing, according to Allianz’s latest Risk Barometer report.
Cyber incidents – such as cyberattacks, IT failure or outage, data breaches, and their corresponding fines and penalties.
Business interruption – including supply chain disruption
Natural catastrophes – including storms, flooding, earthquakes, wildfire, and other weather events
COVID-19 outbreak – such as health and workforce issues, and restrictions on movement
Changes in legislation and regulation – including trade wars and tariffs, economic sanctions, protectionism, Brexit, and Euro-zone disintegration
Climate change – such as physical, operational, financial, and reputational risks resulting from global warming
Fire and explosion
Market developments – such as volatility, intensified competition and new entrants, M&A, market stagnation, and market fluctuation
Shortage of skilled workforce
Macroeconomic developments – including monetary policies, austerity programs, commodity price increases, deflation, and inflation
The disruption brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic has given prominence to this type of coverage, which has also been the point of contention between insurers and their policyholders. In essence, business interruption or BI cover is designed to protect businesses from loss of income and additional costs incurred if their operations are forced to shut down because of an unexpected event. Insurance companies, however, argue that the loss should result from “material damage caused to property.”
How does business interruption insurance work?
Business interruption insurance provides companies financial protection for the losses they suffer because of the disruption to their operations caused by an insured event. It pays out the operating costs while the business temporarily shuts down. These costs include:
Potential revenue
Mortgage or rent on commercial space
Business loan repayments
Employee salaries
Taxes
Some policies also provide coverage for additional expenses related to the closure such as those accompanying the setting up of a temporary location or the training of staff to use new equipment.
For small and medium-sized enterprises, BI coverage is often included in a business owner’s policy, which bundles different coverages companies need, including general liability, commercial property, and workers’ compensation cover.
Business interruption policies typically entail a 48- to 72-hour waiting period to kick in. This is indicated in the policy’s restoration period, which initially lasts for 30 days but can be extended to up to a year.
What are the top causes of business interruption?
A five-year data analysis of insurance claims conducted by leading insurer AGCS has found that fire and explosion were the leading causes of business disruption globally, accounting for 30%, or $6.7 million worth, of all BI losses. This was followed by storms (21%), water damage (12%), machinery breakdown (5%), and flooding (4%).
In terms of business interruption triggers, 52% of respondents said cybercrime, which was driven by the recent spate of ransomware attacks, was the one they feared the most, followed by natural catastrophes (36%), pandemic outbreaks (35%), and transportation and shipping disruptions (30%).
Does business interruption insurance cover COVID-19-related losses?
Whether business interruption policies should cover losses caused by the coronavirus pandemic has been a contentious issue between insurance companies and businesses affected by the outbreak. The insurance industry has maintained that pandemics cannot be covered because of the scale of their impact.
“Pandemics are an extraordinary catastrophe that can impact nearly every economy in the world, so it is hard to predict and manage the risk,” said Sean Kevelighan, chief executive officer at the Insurance Information Institute (Triple-I), in a 2020 statement. “Pandemic-caused losses are excluded from standard business interruption policies because they impact all businesses, all at the same time.”
This, however, has not prevented companies seeking compensation from taking their arguments to court. The University of Pennsylvania Carey Law School’s COVID-19 coverage litigation tracker has recorded more than 2,300 lawsuits over business income coverage, with the majority of lawsuits coming from companies in the food services sector.
Early last year, the UK Supreme Court dismissed appeals by insurance companies in a test case brought by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) on behalf of policyholders. The insurers argued that many BI policies did not cover widespread disruption resulting from the restrictions imposed by the government to curb the spread of the coronavirus in 2020. After scrutinizing non-damage insurance policy clauses, which cover disease, denial-of-access-to-business-premises, and hybrid clauses, the Supreme Court unanimously dismissed the appeals, a ruling that has massive implications for the insurance industry worldwide.
What do companies need to consider when taking out business insurance?
There are several factors that companies need to consider before taking out business insurance. These include:
The company’s business structure
The industry where the business operates
The types of risks the company faces
The company’s size or number of employees
Whether the company has business premises or vehicles
The stock, equipment, and tools the company owns
It would also be helpful for businesses to consult an experienced insurance agent or broker who can give them sound advice regarding which coverages suit their operations the best.
Do you need help finding the right coverage for your business? What types of policies do you think are essential? Use the comments box below to share your thoughts.



