Business insurance in Canada

Insurance Business delves deeper into how business insurance in Canada works in this article. We will give you a rundown of the different policies available and answer the most common business insurance-related questions you may have. For the insurance professionals who frequently visit our site, this can serve as an excellent article for clients of yours that have questions about Canadian business insurance.
Business insurance is an umbrella term for a range of policies designed to protect enterprises from the different risks they are exposed to. It serves as a form of a financial cushion that enables businesses to recoup their losses faster after a sudden and unfortunate event.
But as each business faces a unique set of risks, the type of coverage they require likewise varies. For this reason, business insurance companies in Canada offer companies a tailored selection of policies that matches their specific requirements.
There is no law in Canada mandating business owners to take out business insurance – unless, of course, it is for a commercial vehicle, which is a legal requirement for all Canadian drivers before they can be allowed to hit the road.
Some customers and stakeholders may also require you to purchase certain types of policies for a deal to follow through – and for good reason. Having the right business insurance policies in place helps protect you and your clients against the financial impact of unexpected losses.
Although not compulsory, business insurance can be a smart investment for many Canadian entrepreneurs because of the kind of protection it provides. But as each business is exposed to a unique set of risks and challenges, there is no single business insurance policy in Canada that can cover every need. This is why business insurance providers across the country offer a diverse selection of coverages.
Here are some of the most essential business insurance policies that Canadian businesses should consider, according to industry experts.
1. Commercial general liability insurance
A comprehensive commercial general liability insurance policy, also known as CGL insurance, covers you for third-party injuries and property damage that occur due to negligence in your business activities. It also pays out for claims of damage resulting from a defective work or product, although this may also be covered by standalone product liability insurance.
General liability insurance is primarily designed to protect you from lawsuits. It can also cover cases that relate to libel or slander. CGL insurance pays for legal fees, damages, and out-of-court settlements up to the limits of your policy.
The table below sums up the different types of coverage general liability insurance provides:
2. Professional liability insurance
Also referred to as errors and omissions (E&O) insurance, professional liability insurance protects your business from claims of financial losses from clients due to a service you have provided. These include lawsuits alleging your business of the following:
Negligence
Misconduct
Giving bad advice
Missing deadlines
Failing to deliver goods and services as promised
One important thing to note is that you do not need to commit an actual mistake to be slapped with a claim. Your client only needs to perceive that you were negligent for them to be able to file a claim.
If your business is involved in the following, professional liability insurance may be a smart investment:
Providing advice or services in exchange for a fee
Providing or developing products or devices
This type of coverage is also called malpractice insurance in certain professions, such as doctors and lawyers. Some occupations are also required to take out professional liability insurance to be able to practice legally. These include accountants in Ontario.
You can check out our comprehensive guide on professional indemnity insurance to learn more about this type of business insurance.
3. Product liability insurance
Product liability insurance protects you against claims of bodily injury or property damage caused by a product your business sells, manufactures, or distributes. It covers damages resulting from defective design, manufacturing, and marketing, including incorrect labelling and safety warnings.
The type of coverage product liability provides is commonly included under general liability insurance policies. One important thing to bear in mind, however, is that product liability insurance does not cover service-related claims. For these, you will need to take out professional liability insurance.
Product liability policies are recommended for any business that sells or manufactures a product, including food items. Retailers, both online and in brick-and-mortar locations, are among those who can benefit from this type of coverage.
4. Commercial property insurance
Commercial property insurance – also called commercial building or business property insurance – covers physical loss or damage to your property and its contents caused by an external event, including fire, theft, and vandalism. Your business needs this type of coverage if:
You have an office or commercial space
You own or lease a commercial building, equipment, or inventory
Your building houses computers, hardware, or machinery that you use for business
You have portable electronics – including laptops, tablets, and mobile phones – for your business
You conduct business off-site
Commercial property insurance typically provides the following protection:
Building coverage: Pays out the cost to replace or repair damage to a property your business owns if this is caused by a covered peril.
Tenant improvement coverage: Covers physical renovations and upgrades you make to a property that your business rents which cannot be easily removed such as paint, carpeting, and lighting.
Inventory coverage: Pays out replacement or repair costs of your merchandise and inventory if these are damaged by an insured event.
Equipment and fixtures coverage: Covers the cost to replace or repair equipment, fixtures, and furnishings that were lost or damaged due to a covered peril.
Electronics coverage: Insures electronic devices that you use for business if they are damaged or stolen inside or outside of your office.
5. Commercial vehicle insurance
As the name suggests, commercial vehicle insurance – also referred to as commercial auto or business auto insurance – covers vehicles that you use for your business. These include:
Company cars
Trailers
Trucks
Vans
Every vehicle that you use to transport goods, equipment, materials, tools, and employees should carry a commercial auto insurance policy.
Commercial vehicle insurance provides the same coverage as personal auto policies. Provinces and territories have their own rules and regulations when it comes to mandatory coverage, but there are similarities. These are:
Third-party liability (TPL): Covers the cost of lawsuits if a motorist is responsible for an accident that causes bodily injury, death, or property damage.
Direct compensation property damage (DCPD): Applicable in Ontario, Québec, Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island, this policy covers damages to the vehicle and its contents resulting from an accident with another insured vehicle as long as the policyholder is not at fault.
Accident benefits (AB): Pays out for medical treatments and income replacement if the policyholder is injured in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. It also covers funeral expenses.
Uninsured automobile/motorist (UM): Coverage kicks in if the policyholder or their passenger is injured or killed by an uninsured driver or in a hit-and-run incident. It also covers damages to the vehicle.
This type of business insurance can be absolutely invaluable.
6. Cyber liability insurance
Cyber liability insurance is designed to protect your business against financial losses resulting from cyber incidents. In its cyber insurance guide, the IBC listed the types of coverage a good cybersecurity insurance policy provides. These are detailed in the table below.
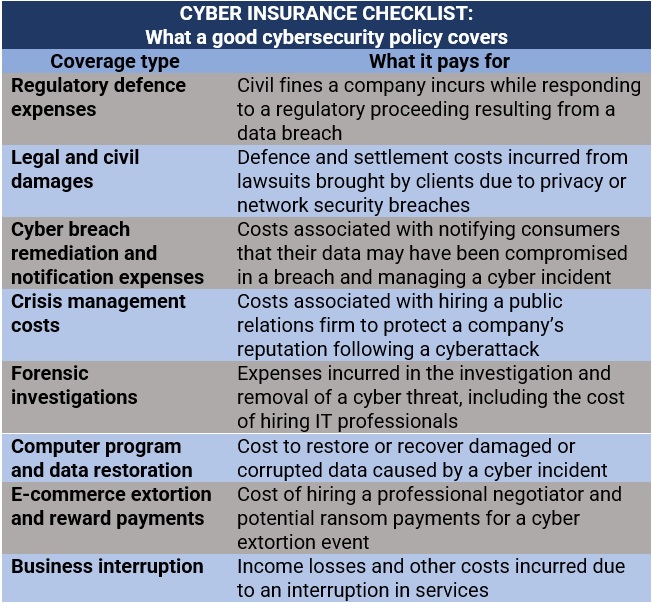
Some industries are more vulnerable to a cyberattack than others. Our latest cybersecurity guide reveals which industries in Canada are most in need of cyber coverage.
7. Directors’ and officers’ (D&O) liability insurance
D&O liability insurance, also known as management liability insurance, is designed to protect the directors and senior management of a corporate or non-profit organization against financial losses resulting from business-related lawsuits. This type of policy pays out for monetary losses from these legal actions, including defence costs, settlements, and fines.
D&O insurance comes in three main types, also referred to as insuring agreements:
Side A: Covers “non-indemnifiable losses” or those situations where the company or business cannot indemnify its directors or officers, either due to bankruptcy or because they are not legally allowed to do so.
Side B: Reimburses a company after it has compensated a director or other senior management for a loss, including defence costs, settlements, or judgments. This is the most common type of insuring agreement.
Side C: Provides direct coverage for a business when both the company and its directors and senior management are named in a lawsuit.
If you’re interested in learning more about how this type of coverage works, you can check out our comprehensive D&O insurance guide.
8. Business interruption insurance
Business interruption insurance, also called BI or business income insurance, provides financial protection for the losses your business sustains due to the disruption of your operations resulting from an insured event. It pays out the operating costs while the business temporarily shuts down. These costs include:
Potential revenue
Mortgage or rent on commercial space
Business loan repayments
Employee salaries
Taxes
Some policies also provide coverage for additional expenses related to the closure such as those incurred for setting up of a temporary location or the training of staff to use new equipment.
9. Life insurance
Life insurance may not be among the usual policies that come into mind when thinking about business insurance in Canada, but corporate-owned life policies provide businesses with several benefits. These include:
Funding buyout agreements
A buyout life insurance agreement is designed to protect a business in the event a co-owner dies. In such an agreement, the death benefit is used to fund buy-sell transactions. This often occurs when the remaining owners are not interested in having the deceased’s family stay involved in the business and the family likewise shows no interest in doing so.
Key employee insurance
Corporate-owned life insurance can cover a vital team member and provide financial benefit to your business at the time of the employee’s death. It is particularly useful for businesses that rely on specific staff for critical tasks. The payout is intended to provide monetary support as the company goes through a transition period to find and train a replacement.
Estate equalization
Life insurance can be used if you want to pass along a business with multiple beneficiaries to a single family member. The process, called estate equalization, allows you to bequeath the entire business to one family member while still leaving something for their other dependents.
If you want to know the other ways businesses can use life insurance to their advantage, you can check out our complete guide to corporate-owned life insurance.
As with other types of insurance, the amount of coverage your business needs depends on a range of factors that may be unique to your operations. The best bet, according to experts, is to take out as much coverage as you can afford. Going for the cheapest option is never advisable as you may later find out that it may not be able to provide enough protection for you to maintain operations.
While not mandatory, taking out business insurance yields a lot of benefits. One of the most obvious advantages is the financial protection such policies provide when unexpected losses occur. These include natural and man-made disasters and costly litigation that can take a huge chunk out of your profits. Having the right types of coverages can help your business recover faster.
Business insurance in Canada is also tax deductible. You can claim the cost of your premiums against your taxable income, reducing the amount you need to pay.
Another benefit of getting business insurance is that it boosts your company’s credibility as most clients and stakeholders prefer working with businesses that they are aware are financially protected.
Business insurance, however, is just one way of mitigating your company’s risks. Still, the best way for you to protect your business’ assets and finances is by pairing the right insurance coverage with good risk management practices.
The need for business insurance is not exclusive to Canadian enterprises. Companies across the globe can maintain some level of financial security by investing in the right type of insurance coverage. Find out how enterprises can use business insurance to address global challenges in this guide.
Do you think it’s smart to invest in business insurance in Canada? Which types of coverages are necessary and which ones can you afford to forego? Share your thoughts in our comments section below.





