12 types of business insurance policies you should consider

12 types of business insurance policies you should consider | Insurance Business America
Guides
12 types of business insurance policies you should consider
There are many types of business insurance you can purchase. But which ones suit your needs? Read on and find out how each coverage works
One of the biggest benefits of having business insurance is the financial protection it offers when unforeseen accidents and calamities threaten to derail your operations. Having the right policy plays a key role in helping your business recover faster. But with the myriad types of business insurance policies out there, how do you know which one provides the correct coverage?
This is what Insurance Business will help you with in this article. If you’re a business owner trying to work out which policies match your unique needs, this guide can prove handy. We will give you a rundown of the different forms of coverage you can access and the kind of protection each one provides. Read on and find out what types of business insurance policies suit you.
Your business faces a unique set of risks and challenges that are different from those of other businesses. That’s why there’s no single policy that can cater to every need.
Business insurance carriers provide a range of policies that can help protect your company. The selection is diverse and the kind of coverage you require depends on several factors including size, scope, and location. Here are some of the most essential types of business insurance policies you need to keep your operations going when accidents and calamities strike.
1. General liability insurance
Although not legally required, general liability insurance is one of the most important coverages to have because of the kind of protection it offers. Also called business liability or public liability insurance, it covers your business financially against claims of bodily injury and property damage resulting from your day-to-day operations.
General liability policies may provide coverage for copyright infringement and incidents that cause reputational harm including libel, slander, and invasion of privacy.
Most policies also offer product liability coverage, which protects your business from lawsuits claiming injury or losses because of a product you sell or make.
General liability insurance pays for the legal and settlement costs if your company has been accused of causing the abovementioned harm. Some policies also cover medical expenses for injuries that happen within your business premises, whether you are at fault, or a lawsuit has been filed.
The table below lists the types of businesses that need general liability insurance.

2. Commercial property insurance
Commercial property insurance helps minimize the financial impact of the damage natural and man-made disasters cause to your business’ on-site physical assets. These include:
Property or building your business operates in
Equipment and technology your business uses
Inventory of products and materials your company stores and sells
Commercial property coverage lessens the disruption of unexpected incidents to your daily operations by providing compensation for the damages and losses. Some policies also pay out a part of lost income if the damage keeps your business from conducting its usual operations. Although not mandatory, this type of business insurance is often a requirement in commercial leasing arrangements.
Commercial property insurance is typically bundled with general liability insurance in a business owner’s policy (BOP), which is a form of small business insurance. Some BOPs also include business interruption coverage.
3. Workers’ compensation insurance
Workers’ compensation insurance protects your business from the financial liability of having to pay for costs resulting from job-related injuries and illnesses. Almost all states in the US require businesses with a certain number of employees to take out this type of coverage.
As a business owner, you are responsible for shouldering the entire cost of coverage. You cannot require your employees to contribute to the premiums. You can click on the link to find out how workers comp is calculated.
Workers’ compensation insurance also follows a no-fault system. This means the benefit an employee receives is not impacted by their or your business’ negligence, although there are certain situations that can lead to workers comp claims being denied.
The table below details what workers’ compensation insurance typically covers.

4. Commercial vehicle insurance
Commercial vehicle insurance is one of several types of business insurance policies that are legally required. This form of coverage works similarly to private auto insurance, but with one major difference: it covers mainly company cars and commercial trucks and vans.
The table below sums up what commercial vehicle insurance typically covers.

Some states allow businesses to purchase UM and UIM coverage separately. There are also business-specific coverages available, including those for lost business income.
5. Health insurance
If your business employs more than 50 full-time staff, you are required to take out health insurance for your workers under the Affordable Care Act (ACA). If you have less than 50 workers, you can access Small Business Health Options Program (SHOP) instead.
Health insurance is designed to help offset the costs of medical treatment by covering a portion of the professional and hospital fees incurred. According to the latest employee health benefits survey by health policy focused non-profit KFF, US companies pay about 83% of their employees’ total health insurance cost for single coverage and 72% for family coverage. These are estimated at $7,911 and $22,463 per year, respectively.
You can check out how health policies work in the US, as well as in other countries that Insurance Business covers in our global health insurance primer.
6. Professional liability insurance
Although not always legally required, professional liability insurance is one of the several types of business insurance policies that are essential for companies offering expert or advisory services.
A professional liability policy protects your business against claims of financial losses resulting from alleged or actual negligence during the fulfillment of a professional service. It covers legal and settlement costs arising from the following:
Service-related mistakes and oversights
Inaccurate advice
Misrepresentation
Breach of contract
Unfinished work
Budget overruns
Personal injury, including libel and slander
Professional liability insurance is mandatory for some occupations. Depending on the industry, it may also be referred to as errors and omissions (E&O) or malpractice insurance. The table below lists some of the professions where this form of coverage is required:
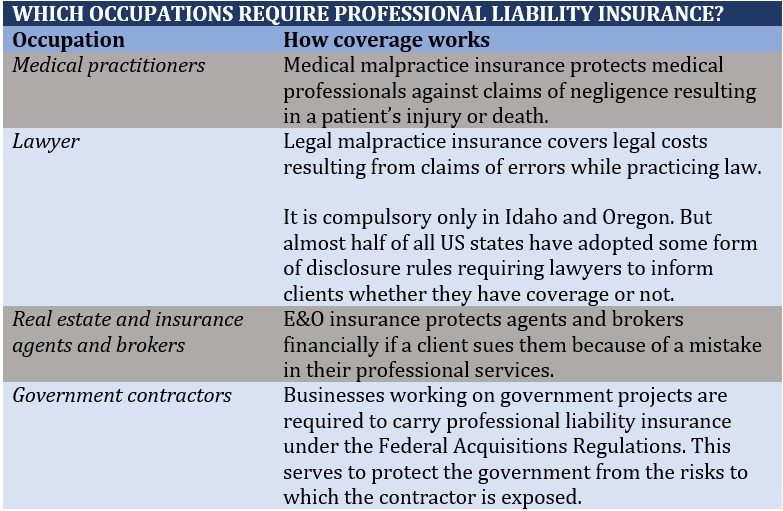
Although not compulsory, the following professions can benefit from having professional liability insurance:
Accountants
Architects
Consultants
Engineers
Financial advisors
Graphic designers
Information technology (IT) specialists
Insurance professionals
Legal professionals
Medical practitioners
Real estate professionals
Software developers
Stylists
Tradespeople
Wedding planners
Professional liability insurance is also an essential form of coverage for limited liability companies (LLC). Find out what other types of business insurance entities like these need in our comprehensive guide to liability insurance for LLC.
7. Directors’ and officers’ (D&O) insurance
D&O insurance is designed to protect the directors and senior management of your company against financial losses resulting from business-related lawsuits. Also called D&O liability coverage, it pays out for monetary losses from these legal actions. These include defense and settlement costs, and fines.
There are three main types of D&O coverage. These are also referred to as insuring agreements or sides, with each offering a different level of protection.
Side A: Covers “non-indemnifiable loss” or situations where your company cannot indemnify your directors or officers. This can be due to bankruptcy or because your business is not legally allowed to do so.
Side B: Reimburses your business after it has compensated a director or other senior management for a loss. This is the most accessed insuring agreement.
Side C: Provides direct coverage for a business when both your company and its directors and senior management are named in a lawsuit. This policy is also called entity coverage.
8. Cyber insurance
Cyber insurance is designed to cover financial losses resulting from cyber incidents. This form of coverage has become a popular risk management tool among businesses, especially with the rapid shift to digital transformation giving rise to constantly evolving cyber threats.
Generally, cyber insurance offers two types of protection:
1. First-party coverage
This type of policy pays out for the financial losses your business incurs because of a cyber incident, including:
The cost of responding to a data breach
Restoring and recovering lost or damaged data
Ransomware attack payments
Lost income resulting from business interruption
Risk assessment of future cyberattacks
The cost of notifying clients about the cyber incident
The cost of providing customer with anti-fraud services
2. Third-party coverage
This type of policy provides financial protection against lawsuits filed by third parties for damages caused by a cyberattack on their businesses. These can include your customers, vendors, and even your own employees.
Third-party policies are also referred to as cyber liability coverage. It typically covers court and settlement fees, as well as regulatory expenses and fines.
9. Business interruption insurance
Business interruption insurance is designed to provide financial protection for the losses your business suffers due to the disruption of your operations if this was caused by an insured event. Also called BI coverage, it pays out the operating costs while your business temporarily shuts down. These costs include:
Potential revenue
Employee salaries
Business loan repayments
Mortgage or rent on commercial space
Taxes
Some BI policies also provide coverage for additional expenses related to the closure. These include the costs of setting up a temporary location or training staff to use new equipment. BI coverage is sometimes included in a business owner’s policy.
Business interruption insurance entails a 48- to 72-hour waiting period to kick in. This is indicated in your policy’s restoration period, which initially lasts for 30 days but can be extended for up to a year.
10. Tools and equipment insurance
Tools and equipment insurance is a type of policy that pays out the costs to repair and replace your business’ tools and equipment if these are stolen, damaged, or vandalized. If your business relies heavily on your tools and equipment to get the job done, then this type of coverage is worth considering.
This policy provides coverage for a wide range of tools and equipment that you use for your business if the items meet these three criteria:
They are movable.
They are less than five years old.
They are worth less than $10,000.
Tools and equipment insurance is often written on an all-risks basis. This means it may cover events not specifically listed in your policy. Some policies provide coverage for the tools and equipment that you lease or rent. There are also policies that pay out for lost income and additional supplies or services needed to keep the project on schedule.
11. Product liability insurance
If your business designs, manufactures, or sells products, product liability coverage may be worth considering. This type of business insurance protects your company against lawsuits from customers claiming losses or injury because of your product. It also covers legal defense costs and compensation if the business is found to be at fault.
12. Excess liability insurance
Excess liability insurance protects your business from catastrophic claims and losses that exceed your coverage limits. If you’re a small business owner, this type of policy can help lessen the risk that a lawsuit or disaster will cause your company to go bankrupt. Some businesses also set this form of coverage as a condition for a lease or client contract. Excess liability insurance is also sometimes referred to as commercial umbrella liability insurance.
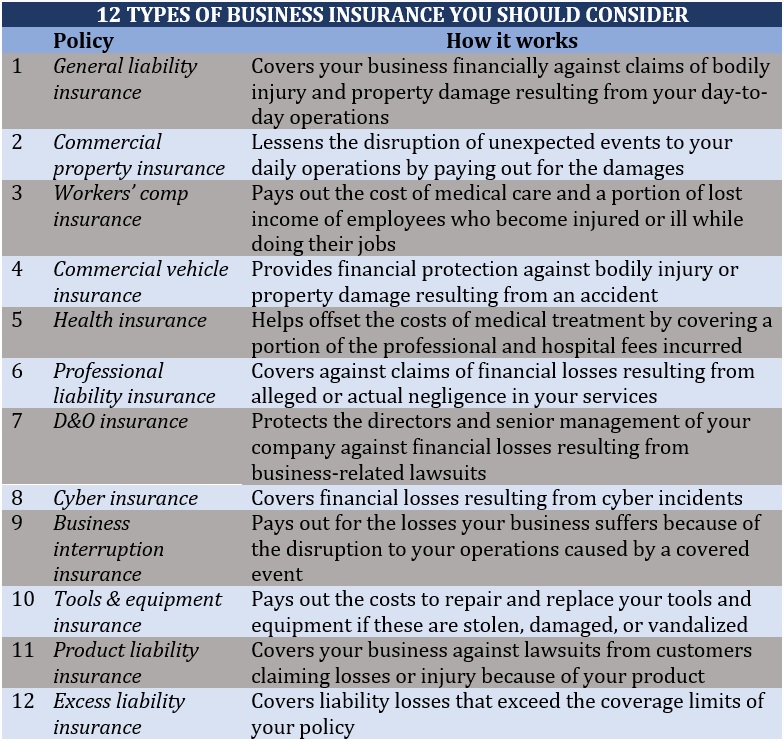
Here’s a summary of the 12 types of business insurance policies every business should consider:
In your day-to-day operations, your business may face situations that can adversely affect your profitability. Mistakes can lead to costly lawsuits, while accidents and calamities can take a huge chunk out of your revenue. Having the right types of business insurance policies can help provide the financial protection you need when unexpected disasters strike.
Another benefit of carrying the right types of business insurance is that it boosts your company’s credibility. The reason is that many stakeholders and clients prefer working with businesses that they know are financially protected.
Taking out coverage, however, is just one aspect of how you can minimize your business’ losses. Pairing the correct insurance policies with sound risk management practices is often the best way you can protect your business’ assets and finances.
What types of business insurance policies do you think are essential? Share your thoughts in the comments section below.
Related Stories
Keep up with the latest news and events
Join our mailing list, it’s free!






