Health care in Spain
ISPOR Europe kicks off this week in Barcelona, Spain. In honor of ISPOR, I will summarize some key attributes of the Spanish health care system based on a 2024 report from the European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies and the Instituto Aragones de Ciencias de la Salud.
Country overview
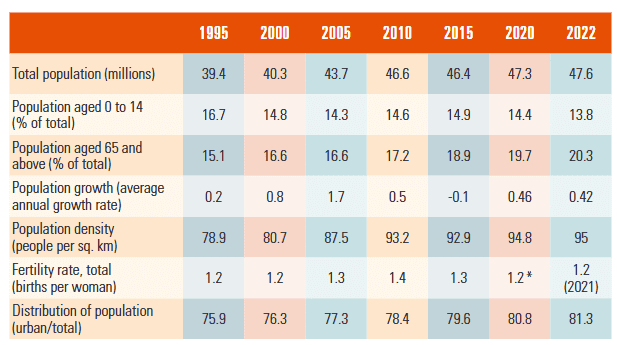
Population: 48.4 million (as of 2023),Life expectancy: 83.2 years (as of 2022), highest in the EUFertility rate: 1.2 (as of 2022), below replacement levelsGDP/Capita (current USD): 29,675 GDP/Capita (purchasing power parity, USD): 46,332Obesity rate: 16%Tobacco use: 19.8% of individuals >15 were daily smokersAlcohol use: 6% of adults regularly engage in heavy drinking (below EU average of 18.5%)
https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/378543/9789289059695-eng.pdf#page=25.21
Healthcare spending
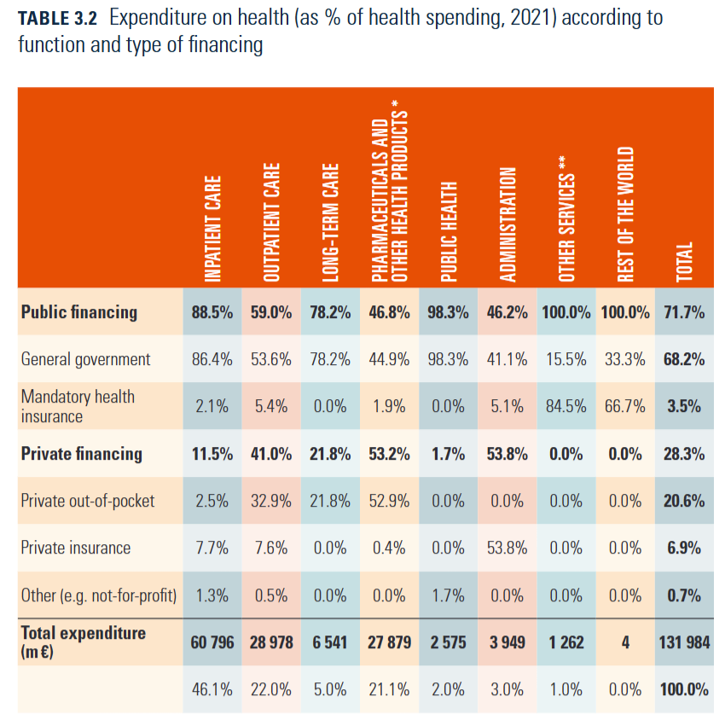
Healthcare spending: €132 billion (as of 2021)Healthcare spending as a share of GDP: 10.8% (as of 2021) Pharmaceutical spending: €12.7 billionPublic healthcare spending as a share of overall healthcare spending: 71.7% (as of 2021).Out of pocket costs: 20.6% of total health spending, largely required for pharmaceuticals and some prosthesesRisk of patient catastrophic expenditures: Very low; among the lowest in the EU due to several protection mechanisms (e.g., exemptions from co-payments), accessible primary care settings, services provided for free at the point of use.Access to specialist. Family Doctor’s act as gatekeepers to specialized and hospital careFocus of health reform since 2018: Widen the population covered by the health system, reduce co-payments, improve scope of covered services, reinforce primary care
 https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/378543/9789289059695-eng.pdf#page=63.21
https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/378543/9789289059695-eng.pdf#page=63.21
Health insurance options
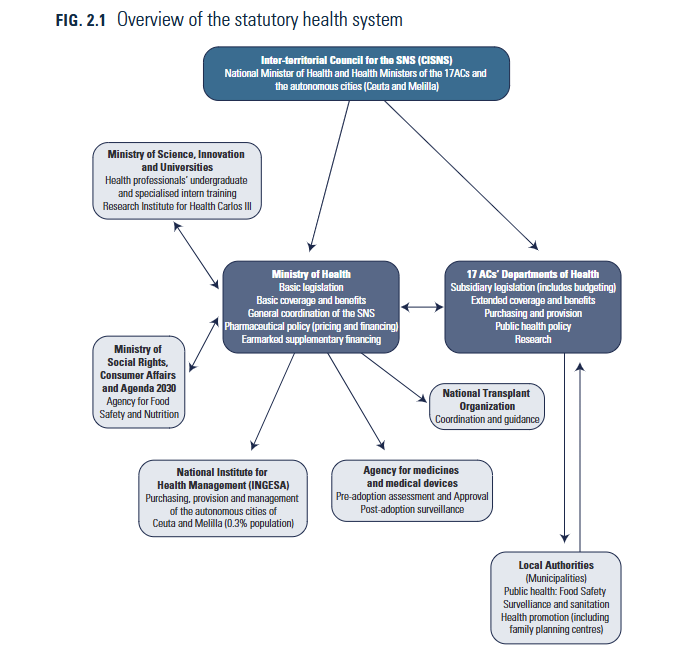
Overview: The Spanish national health system (SNS) provides universal coverage for residents largely funded by taxes. Health competences, however, are transferred to the 17 Autonomous Communities (Comunidades Autónomas). The Ministry of Health is responsible for the overall coordination of the health system under the governance of the Inter-territorial Council for the SNS (Consejo Interterritorial del Sistema Nacional de Salud, CISNS). Insurance eligibility: Based on residency in Spain. (This marks a change from 2012-2017 when eligibility was linked to the legal and employment status of individuals)Can patients opt out of the public health care system (SNS): No, however individuals can purchase voluntary health insurance (VHI) if they desireWhat share of patients purchase supplemental health insurance: 20.8% purchase VHI (as of 2021)
 https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/378543/9789289059695-eng.pdf
https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/378543/9789289059695-eng.pdf
Provider supply:
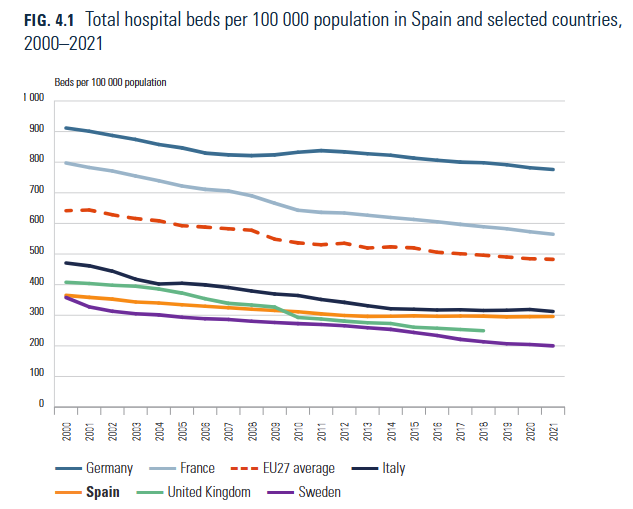
Hospital beds. 296/100,000 inhabitants, of which 81.4% of beds are at public hospitals Nurse vs. doctors: The ratio of nurses to doctors has lingered below the OECD countries’ average ratio (1.4 against 1.97).Key concerns: Shortages in primary care physicians in rural areas, projected future shortages in some specialties (e.g., family medicine, anaesthesiology, geriatrics, psychiatry and radiology)
 https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/378543/9789289059695-eng.pdf
https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/378543/9789289059695-eng.pdf
Recent policy changes and challenges:
Is euthanasia legal?: Yes, as regulated by Organic Law 3/2021Key challenges: Addressing access gaps, (e.g., limited coverage of dental and optical care), and large waiting lists for some services
To learn more, you can read the full report.




